Journal of Multidisciplinary Dental Research
Volume: 4, Issue: 2, Pages: 52-55
Review Article
Sushmitha.P1, Pallavi N.T2, Jumol Joseph3
1Final year BDS Student, Coorg Institute of Dental Sciences, Virajpet
2Final year MDS Student, Department of Prosthodontics, Coorg Institute of Dental Sciences, Virajpet
3Senior Lecturer, Department of Prosthodontics and Maxillofacial prosthesis Coorg Institute of Dental Sciences, Virajpet
Corresponding
Sushmitha P
Final Year BDS Student, Coorg Institute of Dental Sciences, Virajpet
Phone : 9342466688
E-mail : [email protected]
Received Date:11 November 2018, Accepted Date:15 November 2018, Published Date:20 November 2018
3D printing is a phrase used to describe the process of creating 3D object from digital file using a material printer. 3D printing is widely used in dental practice because of its high efficiency, accuracy, precision and reliablility. In prosthetic treatment computerised scanning system and 3D printing system in the form of additive or subtractive manufacturing technology have come largely to replace the traditional techniques of producing prosthetic work. 3D printing is able to produce crowns, FPDs, gingival masks and significantly elevated the rate of success in dental implantology and craniofacial reconstruction. Certified materials like light cured resin, power binder, sintered power, thermoplastic materials and so on are used to fabricate different prosthesis using methods like SLS, stereo lithography, FDM etc.
KEY WORDS: 3D Printing, Additive manufacturing technology, subtractive manufacturing technology
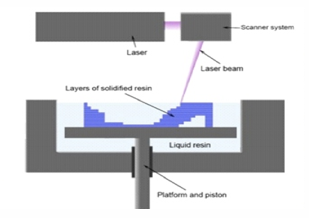
Three dimensional printing also called as rapid prototyping is a form of additional or subtractive manufacturing technology where a three dimensional object is created by laying down or cutting down successive layer of material. Here, the three dimensional object is created using a digital file which is connected to a material printer in a manner similar to printing images on paper. This method is widely adopted in dentistry due to its high degree of detail, fast production, high degree of accuracy and ease. This review article summarises history, materials used, the existing technologies, application in the field of prosthodontics and maxillofacial prosthesis and future trends of digital dentistry.
HISTORY
In 1984, the technology of printing 3D objects from the digital data was first developed by
Charles Hull;
In 1986, he named the technique as Stereolithography and obtained a patent for the technique;
By the end of 1980s
Fused Deposition Modelling [FDM]
Selective Laser Sintering [SLS]
Were introduced;
In 1993, Massachusette Institute of Technology patented another technology named '3 dimensional printing technique';
In 1996, 3 major products 'Genisys' from Stratasys 'Actua 2100' from 3D System and 'Z402' from Z corporation were introduced;
In 2005, Z Corporation launched a breakthrough product named 'Spectrum Z510', which was the first HD 3D printer in the market.
In prosthetic treatment, 3D printing system have largely replaced the traditional techniques of producing prosthetic work. Development of new technique of making prosthetic restoration will lead to long term success of the treatment.
DIFFERENT METHODS WIDELY USED IN DENTISTRY
3D printing technologies used in dentistry includes additive manufacturing technology and subtractive manufacturing technology,
Various additive manufacturing technologies includes
1.Selective Laser Melting [SLM]
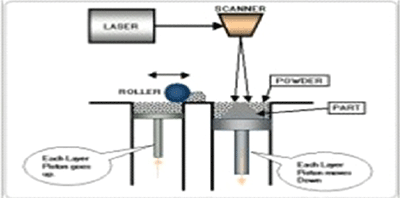
Selective laser melting is a technique where in layer by layer the material is added to generate 3 dimensional object. Successive layers of powder material is added one above the other, using heat generated by computer controlled laser radiation. This method is employed for making metallic frameworks thus helps to encounter the problems caused during casting alloys.
2. Stereolithography
The most popular 3D printing technology invented by Charles Hull in 1980. Stereolithography is an additive manufacturing process using a liquid UVcurable photopolymer. “Resin” and a UV laser are used to build parts a layer at a time. This is the first commercially available 3d printer. It is used in making display models and only disadvantage is that it is sensitive to heat.
3. Fused Deposition Modeling [FDM]
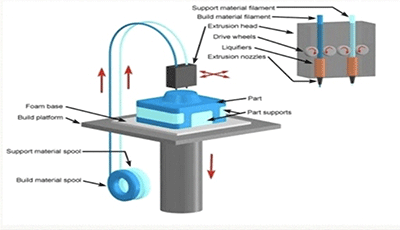
It is an additive manufacturing technology where in the digital file in the form of CAM or Scanned information is used to produce prosthetic restoration. A melted thermoplastic polycarbonate material is added layer by layer to build the object. The melted plastic material combines with each other resulting in finished object which can be used along with wax or acrylic. Different coloured prints are available.
4. Subtractive Manufacturing Technology
It is a process by which 3D objects are constructed by successively cutting away from a solid block of material. subtractive manufacturing can be done by manually cutting the material but is mostly typically done with Computer Numerical Control Machine. The main disadvantage of this method is that there is lot of wastage of materials.
USES OF 3D PRINTING IN PROSTHODONTICS AND MAXILLO FACIAL PROSTHESIS
3d printing is extensively used in the field of prosthetic rehabilitation due to its accuracy, high degree of detail and ease.
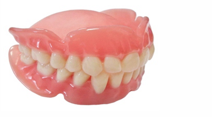
1.3d printing in the fabrication of Complete Dentures.
There are 2 methods for the fabrication of complete denture using 3d printing.
In the first method, impression is made in the patient's mouth which is then scanned and transferred into a programme or a digital file. In the second method the impression is made and is poured with stone and then this model is scanned and transferred into digital file. Using this digital file the complete denture is manufactured with the aid of desired material printer.
2. 3d printing in the fabrication of RPD framework
The impression is made and the cast is poured which is scanned and converted to digital file. Then RPD design is planned with all essential components including clasp and rests required for support, retention and connection of the denture. Next softwares are used to digitally survey the cast according to the selected path of insertion and the undesirable undercuts will be removed. Later RPD components are created as planned and finally the framework is printed using a 3D Printer. Various materials like metals and polycarbonate is used. Employing 3D printing technology will increase the speed and accuracy of the denture fabricated.
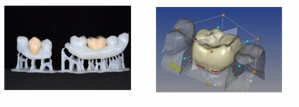
3. Fabrication of crowns and FPD using 3D printing
Employment of 3d printing technique allows better visualization and design of the restoration. Natural teeth, soft tissue around the abutment and edentulous area is scanned and is digitalized. Maxillary or mandibular cast along with the dies are printed first, followed by printing the Gingival tissue separately. Later, the crown is milled. The printed components are restored intraorally. An intrim restoration is usually made before the final prosthesis for patient's acceptance. Similar protocol is followed for fabrication of final prosthesis. Mostly liquid photopolymerizing material is used.
4. 3D printing in dental implant
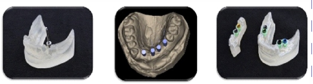
3d printed model of dental implant allows for proper angulation, depth and accurate placement of implant. It also allows for precise presurgical fabrication of temporaries and translucency allows for precise preplanning. The intra oral data is collected using CBCT and then the exact location of implant placement is known considering the quality of the bone present and anatomy of the jaw This surgical guide is 3D printed which helps to know the exact location of implant placement. This customized surgical guide will help in better outcome and aid to success of the treatment. Later with the help of intraoral scanner or digital impression or scanned cast the crown is designed and then milled.
5.3D printing in maxillofacial prosthesis
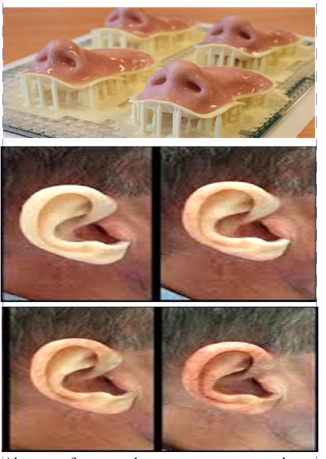
Absence of parts such as ear, eye, nose etc. due to trauma and congenital disorder may be present. In such cases 3d printed prosthesis can be given to restore the missing parts. Such Prosthesis can be customized to clearly understand the complexity and anatomy of the patient. The opposite side can be scanned and duplicated so that a better symmetry can be obtained which will increase the patient's acceptance.
NEWER TRENTS OF DIGITAL PRINTING
The most advanced 3d printing application that is anticipated is the Bioprinting of complex organ. in which implants or living organs are printed in human body during operation, is another anticipated future trend. bioprinting for repairing external organs, such as skin, has already been taken place. This approach could possibly advance to use for in situ repair of partially damaged, diseased or malfunctioned internal organ.The hand held 3d printers for the use in situ for the direct tissue repair is an anticipated innovation in this area. Advancement in robotic bioprinter and robot assisted surgery may also be integral to evolution of this technology.
Along with these, a new superior Nylon 680 which is a high medical grade nylon is now available for 3D printing. Recently 2 newer materials known as DENTCA Denture Base 2 and DENTCA Denture Teeth [used together] are available which is the first 'Food and Drug Administration' approved Class 2 materials for the fabrication of 3d printed dentures.
CONCLUSION
3D PRINTING is substantially employed in dentistry. Dental prosthesis can be fabricated layer by layer directly from a computer model easily and rapidly by various technique. This technique is a revolutionary change in fabrication of dental prosthesis.
Sushmitha et al.,3D Printing technology.2018:4(2);52-55
Subscribe now for latest articles, news.