Journal of Multidisciplinary Dental Research
Volume: 4, Issue: 1, Pages: 21-23
Original Article
Neveda Baskeran1, Subramanian EMG2
1Professor And Head, Department Of Pedodontics , Saveetha Dental College , Chennai , India
2Cri, Saveetha Dental College , Chennai , India
Corresponding
Neveda Baskeran , Cri ,
Saveetha Dental College , 162, Poonamalle High Road , Velappanchavadi , Chennai 600077. Email Id:- [email protected]
Received Date:26 October 2018, Accepted Date:24 November 2018, Published Date:26 November 2018
AIM:- To assess the behaviour of children with single and double hair whorls during dental treatments.
OBJECTIVE :-To compare the behaviour and cooperative ability of children with single and double hair whorls.
BACKGROUND :- Various researches have been done to assess the influence of minor anomalies on the hyperactivity of children. Minor anomalies like head size, hypertelorism , hair line , electric hair, low set ears with adherent lobes, malformed pinnas and number of hair whorls, were compared with the hyperactivity of children . As there were no evident research done comparing the number of hair whorls and behaviour of children in a dental setup, a pilot study was done . The study was done in 20 children who came to Saveetha Dental College for treatment. The number of hair whorls were correlated with behaviour of children during their subsequent dental treatments. Wright's modification of Frankl's behaviour rating scale was used to assess the behaviour .
REASON :- This helps the dentist to be prepared and plan treatment according to the number of hair whorlsof children.
Key words: behavior, hair whorls
Whorls are anatomical features found anywhere in the human body but mostly on the head of an individual. They can be clockwise or anticlockwise in symmetry(1).There are various factors which contribute to the direction of hair whorls. The handedness of an individual is compared with the direction of hair whorls. They suggest that it depends on learned behavior and genetics(2) Various studies done in cattles and dogs , correlates hair whorls with various factors like behaviour, handedness, etc .The relationship of hair whorls with brain development is correlated with the fact that, they arise from the same ectodermal embryonic origin(3). There is a belief stating that children with more than one hair whorl are more mischievious and naughtier than those with a single hair whorl .Hence, the behaviour of a child in the dental chair is compared based on the number of hair whorls.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Aquantitative pilot study was conducted to assess the behaviour of the children using Wright's Modification of Frankls Behaviour rating scale. The study was conducted in the outpatient section of Department of Paediatric Dentistry in Saveetha Dental College , Chennai, India .The procedure and aim of the study were explained in advance to the parents.
INCLUSION CRITERIA
- Children of age 3-13 years of age
- Children with physical or mental disability
STUDY DESIGN
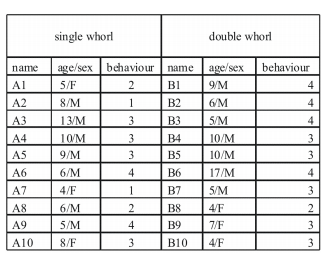
The relation of behaviour to the number of hair whorls wereevaluated with the help of proformas filled by the dentist. 20 outpatients were examined out of which 10 had single whorl and the other 10 had more than one whorl. The required data (i.e) name, age , gender, casesheet details, treatment done and the behaviour were obtained from the dentist and noted accordingly .
CLINICAL EXAMINATION
The dentist examined the children and the treatment was planned accordingly. Their behavior during treatment was assessed using Wright's Modification of Frankls Behaviour rating scale.
RATING 1 :- Definitely negative (--) Refusal of treatment, crying forcefully, fearful or any overt evidence of e x t r e m e negativism.
RATING 2:- Negative (-) Reluctant to accept treatment, uncooperative, some evidence of negative attitude, but not pronounced , (i.e) sullen, withdrawn.
RATING 3:- Positive (+) Acceptance of treatment ;at times cautious , willingness to comply with the dentist , at times with reservation but patient follows the dentist's directions cooperatively.
RATING 4 :-Definitely positive (++) Good rapport with the dentist , interested in the dental procedure , laughing and enjoying the situation Based on the above scale the behaviour during the consecutive treatments were evaluated. The data was then compiled for further evaluation .
RESULTS
The data collected was tabulated .
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS
P value and statistical significance The two tailed p value equals 0.982
Statistical analysis of the results showed that the number of hair whorls did not have a statistical impact on the behavior of children during dental treatment.
DISCUSSION
Whorls are anatomical structures found mostly on the head . This study was conducted based on a belief that children with more than one whorl were more naughty and mischevious than those with single whorl. The results showedthat there is no significant impact of number of whorls on the behaviour of the child . On contrary, it is evident that patients with more than one hair whorl cooperated better than those children with single hair whorl. Various studies were done to assess the relation between hair whorls and behaviour , which used external anatomical feature as a tool to assess behaviour(4). The studies to assess the link between behaviour and hair whorls in a dental setup has never been attempted before . This pilot study was conducted to analyze if there is any significant changes in the behaviour of children . It was proved that sex and age had no significant changes in the behaviour of a child .In fact youngchildren cooperated better than older children . This pilot study analysed the data on a smaller scale . Further research is intended to be done on a larger scale to give significant values to the research . Further research with more sample size ,under specific criterias like age, sex predilection is to be carried out for obtaining significant values to the research .
CONCLUSION
The number of hair whorl of children had no impact on their behavior during dental treatment .
Baskeran et al., Assessment of behaviour of children with one or more hair whorls during dental treatment.2018:4(1);21-23
Subscribe now for latest articles, news.