Journal of Multidisciplinary Dental Research
Volume: 4, Issue: 1, Pages: 45-47
Case Report
Sendhil Kumar V1, Krupashankar2
1Postgraduate, Department of Oral Medicine and Radiology, Coorg Institute of Dental Sciences.
2Professor, Department of Oral Medicine and Radiology, Coorg Institute of Dental Sciences
Corresponding author
Dr. Sendhil Kumar
E-Mail: [email protected]
Received Date:01 October 2018, Accepted Date:26 October 2018, Published Date:15 November 2018
Amelogenisis imperfecta is a congenital disorder that affects the enamel formation causing discoloration of teeth, causing pits and grooves in enamel structure leading to rapid wear and breakage of enamel structure. Here we present a case of Amelogenisis Imperfecta (hypo maturation type) on the basis of classical clinical and radiological features.
The enamel is the only ectodermal derivative of the tooth and hardest tissue in human body. Inorganic constituents account for 96% by weight and they are mainly calcium phosphate in the form of hydroxyapatite crystals.1 The physical properties and physiological function of enamel are directly related to the composition, orientation, disposition, and morphology of the mineral components within the tissue.2 During organogenesis, the enamel transitions from a soft and pliable tissue to its final form, which is almost entirely devoid of protein. The final composition of enamel is a reflection of the unique molecular and cellular activities that take place during its genesis. Deviation from this pattern may lead to amelogenesisimperfecta(AI).
CASE REPORT
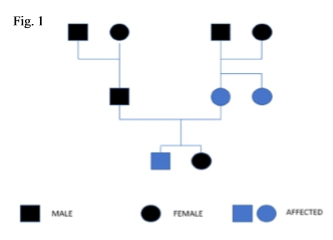
An 28-year-old male patient from Waynad reported to the Department of Oral Medicine and Radiology, Coorg Institute of Dental Sciences, Virajpet, with the chief complaint of discoloration and breaking of teeth since childhood.The patient had the problem since birth did not seek any treatment previously, thinking that his mother had same condition and didn't cause any problem. Since past few weeks he had sensitivity of teeth and breaking away of teeth for which he consulted Govt institution and underwent treatment. On enquiry, it was revealed that his deciduous teeth were also similarly discoloured, and he had a younger sister of twenty-four years, doesn't have the same condition. The patients mother and mother's sister suffered from similar condition and didn't undergo any treatment. The pedigree chart could be constructed as in Figure 1.
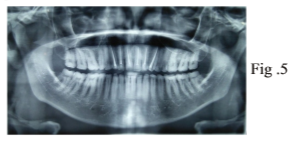
IOPAR taken six months back shows extensivecircumscribed radiolucent lesion at the cervical region of 26 and with cervical resorption of distal aspect of 25.
Past medical history was non-contributory and dental history patient visited government dental college, Trivandrum for same reason and was advised root canal treatment for same. Patient discontinued treatment there due to inconvenience in travelling the distance and came to our institution seeking treatment for same.
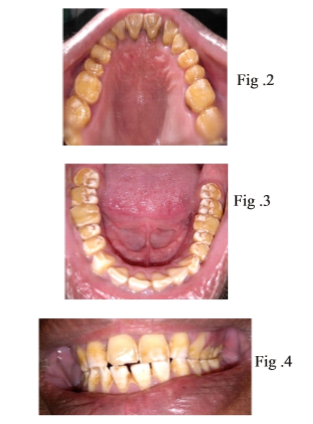
Intra oral examination revealed generalised reduction in thickness of enamel with yellowish brown discoloration of tooth structure. The surfaces of teeth appeared rough with chipping of enamel and exposing the dentin surface which was more prominent on occlusal aspect of the teeth. The region where enamel was present diffuse pitting was seen. All the teeth were present and there was no caries. Examination of periodontium revealed presence of chronic generalised marginal gingivitis with moderate calculus deposition.
A provisional diagnosis of Amelogenesis imperfecta Hypo maturation type was proposed with a differential diagnosis of enamel hypoplasia, dentinogenesis imperfecta and dentin dysplasia.
Radio graphic investigation included an orthopantomogram which showed more reduction in radiopacity of enamel as it was difficult to differentiate between dentin or more radiolucent than dentin. The pulp chambers appeared normal. Radiopacities indicative of root canal treatment was seen irt 11,12,13,21,22,23. The ground section being gold standard was not possible in this case as no teeth was indicated for extraction.
Esthetics along with functional limitations were the reason the patient had come to the hospital for treatment.The treatment proposed for him ranged from bonded veneer restorations to tooth preparations for the placement of a full crown.
DISSCUSSION
AI is a condition that effects the dental enamel as well as some extra oral and oral tissues. The prevalence varies from one in 700 to one in 14000.3 Amelogenesis imperfecta is a genetic anomaly arising from mutations that may have occurred in one or more of four candidate genes that play some role in enamel formation: amelogenin (AMELX), enamelin (ENAM), enamelysin(MMP20), and kallikrein 4 (KLK4). The mutation may be inherited in an autosomal dominant or recessive manner, or it may be inherited in an X-linked pattern.4
CONCLUSION
The varying etiology of AI conjures a wide array of clinical features whose restorative management poses a challenge for dentists. As both esthetics and function are compromised in these patients, their management usually involves complete oral rehabilitation by way of full coverage crowns, direct and indirect veneers, and bonded esthetic restorations, depending on the condition of the individual tooth and the age of the patient. If the treatment is delayed, a loss of usable crown length occurs. In those patients without sufficient crown lengths, full dentures; often become the only satisfactory approach. Thus the dentist has to diagnose the condition as early as possible for early intervention and treatment planning for the condition.
Kumar et al., Amelogenesis imperfecta: a case report.2018:4(1);45-47
Subscribe now for latest articles, news.